✅ If you think you’ll find this interesting, check our our newsletter for more!
Finding the right contraceptive method for you can be challenging and it can feel confusing knowing where to start. Some women find the right contraceptive method straight away whilst others have to trial lots of different options to find the right match.
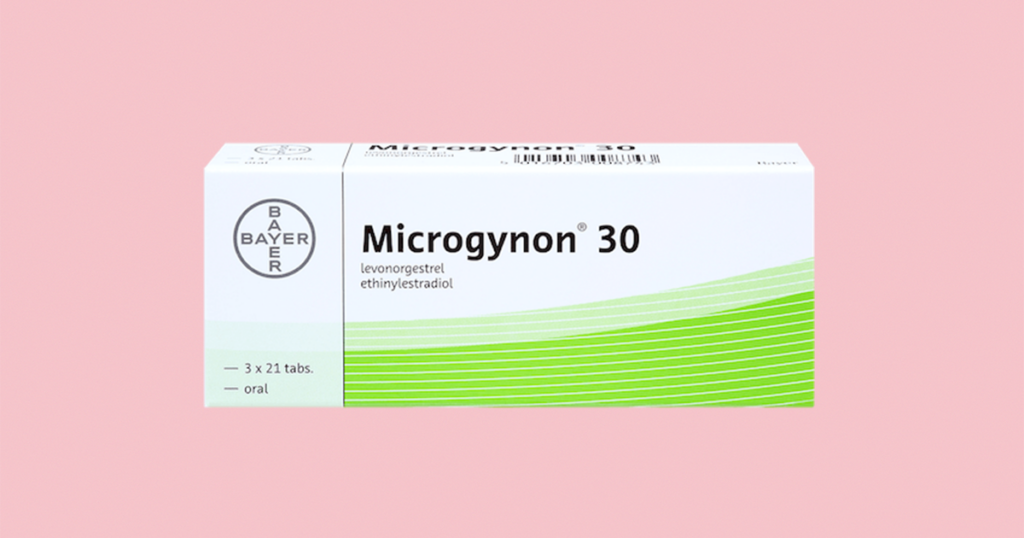
Microgynon is one of the most well known brands of combined contraceptive pills but it has the same hormones as other contraceptives pills such as Rigevidon, Levest and Ovranette. These combined pills tend to be the first type offered by healthcare professionals when starting a combined pill as they have lowest risk of blood clots.
What is Microgynon?
The hormones in Microgynon, Rigevidon, Levest and Ovranette are oestrogen (ethinylestradiol) and progestogen (levonorgestrel). All combined pills prevent pregnancy by stopping ovulation, making the fluid in your cervix thicker and preventing the lining of your womb from thickening.
Traditionally with Microgynon you take one pill a day for 21 days and then have a 7 day break. However you have the option to shorten or avoid the break and take your pill continuously. You can buy the Microgynon pill here at The Lowdown
What is Microgynon ED?
For those who want to take a pill every day for ease, there is also a Microgynon 30 ED (every day) pill which consists of seven dummy pills, which are a different colour from the other 21. The dummy pills represent the break week when you have a withdrawal bleed.
This makes it more difficult to use continuously or back to back (you would have to omit the dummy pills) which is a useful way to avoid periods and period related problems.
How effective is Microgynon?
When we look at how effective a contraceptive method is we look at typical and perfect use. At the Lowdown, we have come up with an easy guide about different contraceptives to help you to find the most effective option. If we look at 100 sexually active women taking this type of pill for a year, with perfect use less than 1 will get pregnant but if we look at typical use 7 women will get pregnant during that year.
It is important to think about how good you will be at remembering to take a pill every day when you are choosing which contraceptive method is best for you. There are now apps available to help you remember to take your pill. We recommend taking your pill when you do something routinely every day like brushing your teeth to help build the habit.
Side effects of Microgynon
As with all contraceptive methods, women may experience a range of different side effects or none at all.
The below side effects are some of the most frequently reported from users of Microgynon;
- Tender breasts (52%)
- Vaginal discharge (52%)
- Enlarged breasts (43%)
- Period like cramping (41%)
- Vaginal dryness (38%)
Take a look at our Microgynon side effects page to see what users of Microgynon said about changes to their mood, bleeding, sex drive, and weight. You can also check out our reviews page for stories about how other users got on with Microgynon.
Risks of taking Microgynon
One rare but serious risk of the combined pill is blood clots, this includes deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism. The risk of blood clots is highest when you first start a combined contraceptive, mainly as it might highlight an underlying blood clotting problem that you may have or be due to hormonal change to proteins in your blood.. It is also important that if you have a long period of immobility such as after a major operation or on a long-haul flight, be aware of increased risk of blood clots.
While the risk is very low, look out for the symptoms of a blood clot. These include stabbing pains or swelling in one leg, pain on breathing or coughing, coughing up blood, sudden breathlessness or chest pain.
The combined pill may also increase your blood pressure so you will need to have this checked before you are prescribed the pill and normally once a year whilst using it. Use of the combined pill is also associated with small increased risks of breast cancer and cervical cancer which reduce with time after stopping.
For more information about the range of combined pills available have a look at our Lowdown page.
Tags
-
FSRH Clinical Guideline: Combined Hormonal Contraception (January 2019, Amended November 2020)
-
Bateson, D. et al. Risk of venous thromboembolism in women taking the combined oral contraceptive: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Volume 45, No.1, January/February 2016 Pages 59-64
Sophie is a Cardiff University- trained journalist who is passionate about sharing womens’ contraception stories in the hope that it will connect with others.
You can find her on Twitter.